I am live blogging so hit refresh to see more.
Speakers: Ben Armstrong, Jose Barreto, Rob Hindman
Primary focus of the session is upgrading from from (Windows Server 2012) WS2012 Hyper-V to (Windows Server) WS2012 R2 Hyper-V. There are scale requirements.
Advice: deploy new designs with upgrades in mind – faster release cadence from Microsoft.
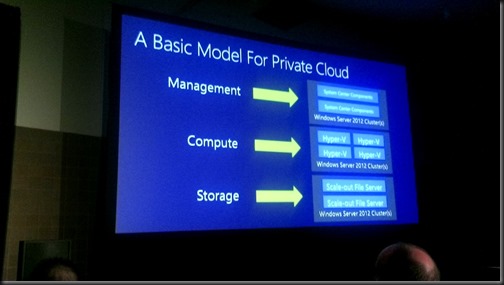
Fabric
- System Management: System Center on Hyper-V
- Compute: Hyper-V
- Storage: Scale-Out File Server on block storage or Storage Spaces
Upgrade System Center First
It will manage the existing cloud/hosts and enable upgrades.
Question: will users notice if a given SysCtr component is offline for a brief period of time.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj628203.aspx …. should be updated with WS2012 R2 upgrades. Remember to turn on OpsMgr maintenance mode during upgrades!!!
Upgrading SCVMM
- Ensure that SCVMM is configured with a seperate (preferably external) database server
- Uninstall SCVMM 2012 SP1 – leave library/libraries and SCVMM database in place
- Install SCVMM 2012 R2, and connect to existing database.
Your outage time is minutes. Deploy SCVMM in a VM. And deploy SCMM as a HA cluster (pretty sensible in a true cloud where SCVMM is critical to self-service, etc).
Up comes Jose Barreto …
You could do Compute upgrade next but ….
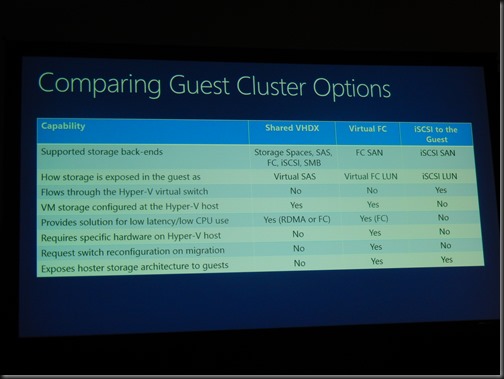
Upgrading Storage
Tools:
- Storage migration
- Copy Cluster Roles Wizard
- Upgrade in place
- PowerShell scripting
Options for storage upgrade
Extra hardware. No down time: (easiest) migrate storage. (2nd fave) Limited downtime: copy cluster role.
Limited extra hardware: No downtime: (4th fave) Migrate pools. (3rd fave) Limited downtime: upgrade in place.
Option 1 – Migrate Storage
- Setup new 2012 R2 storage cluster
- Configure access to new cluster
- Storage migrate every VM (Live Storage Migration to new storage platform)
Easy and zero downtime. Easy to automate. Network intensive. Needs new storage platform.

Option 2 – Copy Cluster Roles
Some downtime, but very quick.
- Setup new 2012 R2 storage cluster. Connect new cluster to existing storage.
- Copy cluster roles.
- Downtime begins: Offline roles on old cluster. Online roles on new cluster
- Down time end.
Limited downtime. No data moved on the network. Limited additional h/w. Good for impatient admins.
3 – Upgrade in place
1 – Prepare
- HA degraded
- Evict a node from clsutger
- Upgrade/clean install evicted node
- Create new cluster with evicted node
2 – Migrate …. do the previous Cluster Role Copy process.
3 – Rebuild the last remaining node in old cluster and join the domain.
You lose HA for a time. You could buy 1 extra server if that’s an issue and recycle 1 old server when the process completes.
4 – Move Pools
No downtime. Moves data over the network. Limited additional hardware.
1 – Split cluster
- Evict node(s) on old cluster – if you have 4 nodes then you can evict 2 nodes and keep HA.
- Upgrade evicted nodes to new version
- Forma site-by-side cluster with shared access to the storage
2 – Migrate storage
- Evacuate a pool of VMs using storage live migration
- Evict pool from old cluster
- Add pool to new cluster
- Use storage live migration to move VMs to pool on new storage cluster
- Repeat until complete
You need extra storage capacity to do this … you are moving VM files from pre-evicted pool to other pools in the older cluster, before moving them back to the pool in the new cluster.
Also have 1 pool (minimum) per node member in the storage cluster.
3 – Finalize
- Destroy the old cluster
- Rebuild idle nodes and join to new cluster
Why have 3 or 4 nodes …. you provide some cushion for upgrade/migration scenarios.
Note: you can use VMM for any LMs or storage LMs.
Back to Ben for the compute upgrade.
Cross-Version Live Migration
Provides simple zero-downtime way to move a VM across to a new platform.
You can use one of many methods to get a new WS2012 R2 cluster … evict/rebuild, brand new, etc. Then you can do a Cross-Version Live Migration.
In the demo, Ben fires up the VMM 2012 R2 console (he can also do this using the built-in Server admin tools, e.g. Hyper-V Manager). VMM is managing the WS2012 hosts and the WS2012 R2 hosts. He can do a LM of the VM from the old hosts to the new hosts. Here’s the benefit of upgrading System Center first. It can manage the new platform and leverage the new WS2012 R2 features.
Another thing with SysCtr …. leverage your templates and logical networks to standardise hosts. New hosts will be identical config to the old hosts, e.g. the VM Network will have the same name so the VM won’t go “offline” when it has moved to the new hosts.
You can stage the upgrades
WS2012 R2 hosts and use WS2012 R2 storage. WS2012 hosts can use WS2012 R2 storage.
Upgrade the Guest OS Integration Components
The world won’t end if you don’t …. some new features won’t work if they rely on the new ICs. Start planning the upgrade around your next maintenance window or planned upgrade. You can deploy the ICs without rebooting immediately – but the new version won’t work until you do reboot.
d:supportamd64setup.exe /quiet /norestart …. Aidan – add that as an app in ConfigMgr if you have a private cloud, and send the sucker out to a collection of Hyper-V VMs, with a predefined maintenance window.
Cluster Rebuild Options
If you have scale, you can do 2 nodes at a time to maintain HA.
If you are small then do 1 node at a time, but lose HA.
Buy some new hardware to act as the “seed” for a new cluster, and evict/rebuild the older cluster. You maintain HA, but at a relatively small cost. You can recycle the last 2 nodes in the old cluster.
For a small shop, take advantage of save state compatibility through:
- In place upgrade
- Virtual machine import
Funnily enough, a HUGE shop might also use that last option. They could also:
- Save state the VMs
- Reconnect the storage to new hosts
- Import/register the VMs
Cluster Validation
Will require downtime unless you are using Windows Server File Storage. Note that a cluster is not supported until you have a passed cluster validation report. Block storage will bring down the disks when validated.
Windows Server 2008 R2 to 2012 R2
Here comes Rob Hindman … who has the best job in the world, apparently, cos he works with Ben and Jose 
Copy Cluster Roles Wizard
This will move the cluster roles from 2008 R2 to 2012 or 2012 R2. Basically, it allows you to move cluster resources to a cluster from another cluster that is 2 levels back, e.g. 2008 R2 to 2012 R2.
- You can test the copy without impacting production/customers
- The process is reversible if you encounter issues
- Assumes that your storage will be reused
- Does not copy data … it remaps disks
You form a new cluster and connect it to the old storage. You run the wizard against the old cluster. You copy the roles. Then you bring online the roles in the new cluster after off-lining them on the old cluster. Then you can remove the old cluster.
Supports lots including:
- Hyper-V VMs/VM configuration
- SOFS
- CSV
- Storage pools/spaces
Does not do CAU or Task Scheduler Tasks.
PLEASE READ THE REPORT that the wizard creates. There might be fix-up steps, e.g. network settings.
Demo:
Does a W2008 R2 – WS2012 R2 migration. You have to migrate 1 LUN (CSV) at a time. Make sure that your destination cluster can handle the VM workload that is on the CSV that you are migrating. If it detects a VM workload, it’ll prompt you to select a destination virtual switch. The copy is done … no downtime, yet. Read the report, as advised.
The VM appears on the new cluster, but it’s showing as off. So is the CSV. On the original cluster, you take the resource offline – shutdown the VM. Take the CSV disk offline. Some customers prefer to unmask the CSV at this point from the old cluster. Bring the CSV online in the new cluster. Then power up the VMs on the new cluster. Done!
Other than a MS IT VPN blip, the demo worked perfectly.
Summary
You can do the upgrade with no downtime if you have lots of resources. More likely you’ll do with with few/no new resources with minimal downtime.
Q&A
Clarification: you are not abandoning CSV. You are putting an active/active file server cluster (SOFS) and SMB 3.0 between the Hyper-V hosts and the CSVs. This layer adds sooooo much and makes you very flexible.
Smaller deployments, such as 2 nodes, then you continue to direct attach your CSVs to your hosts, e.g. CiB Hyper-V deployment.